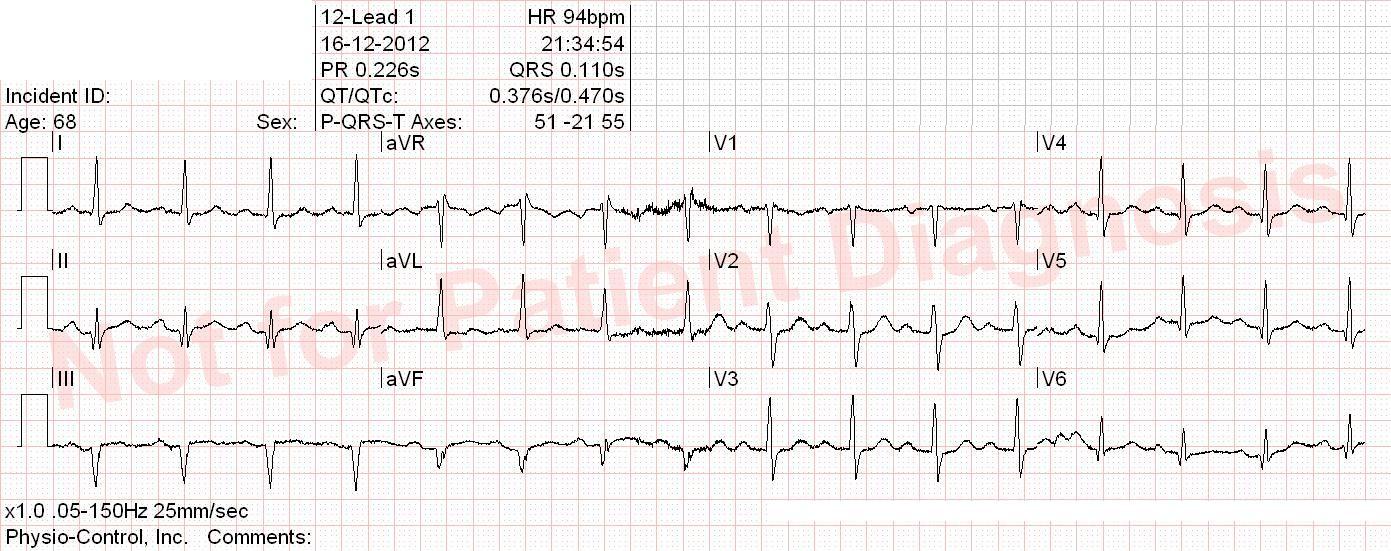
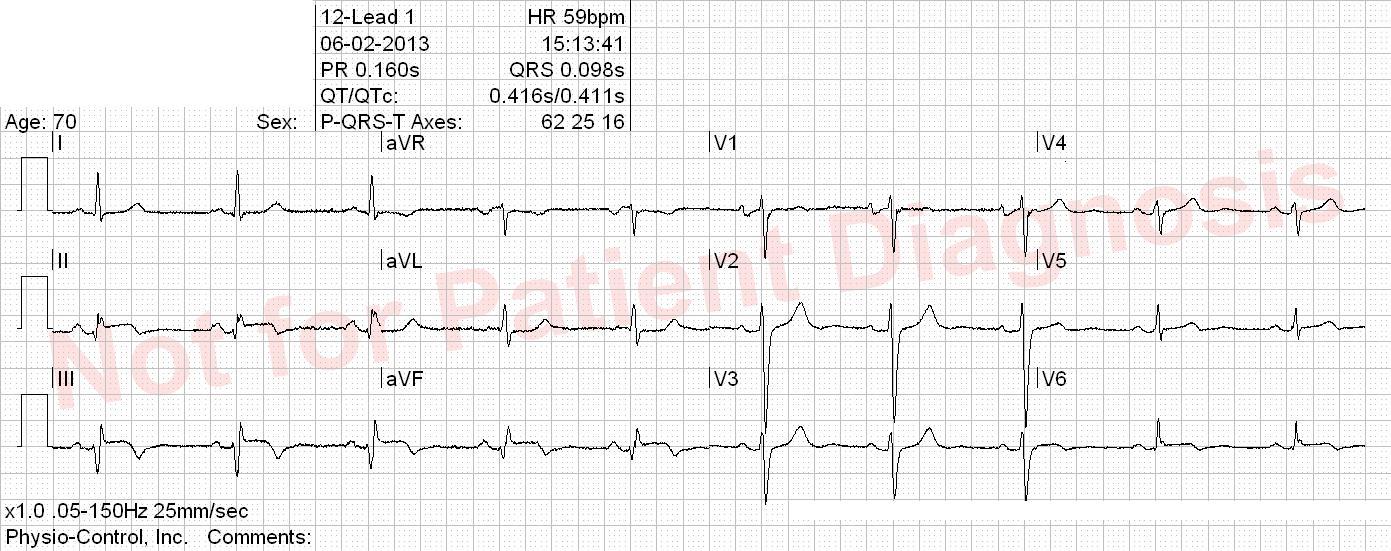
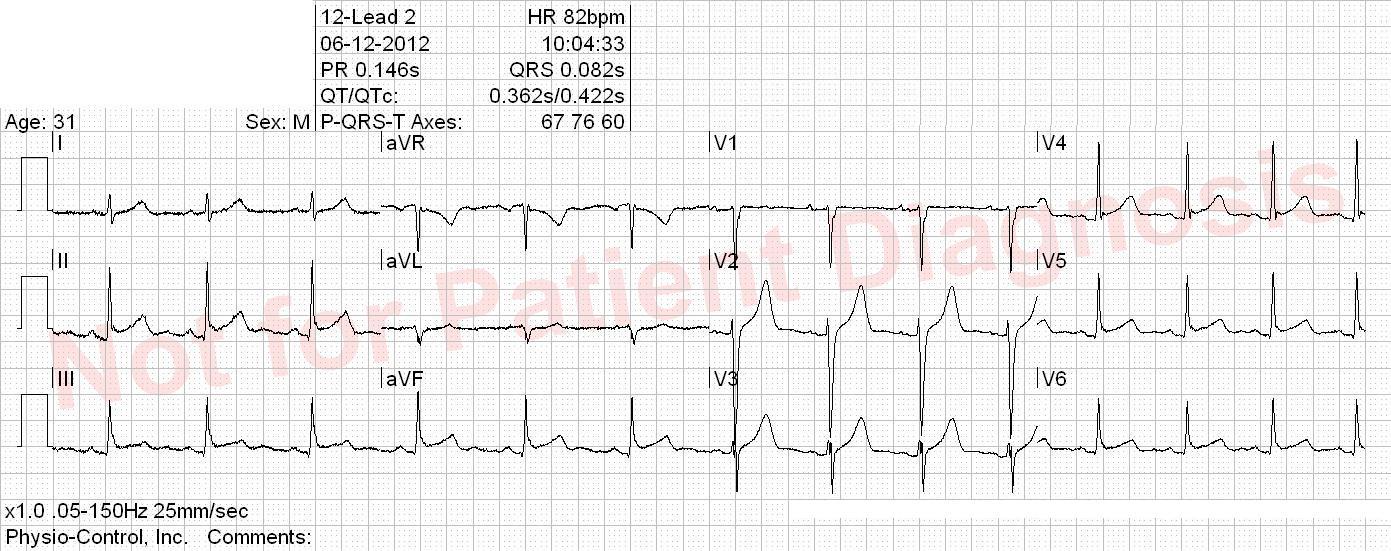
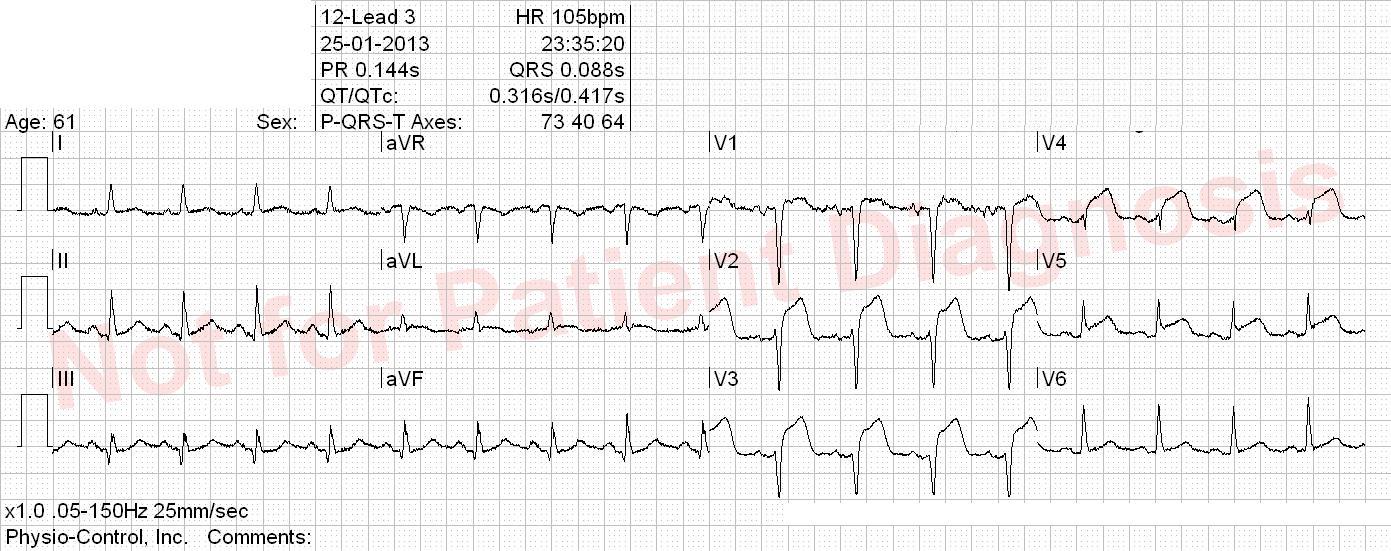
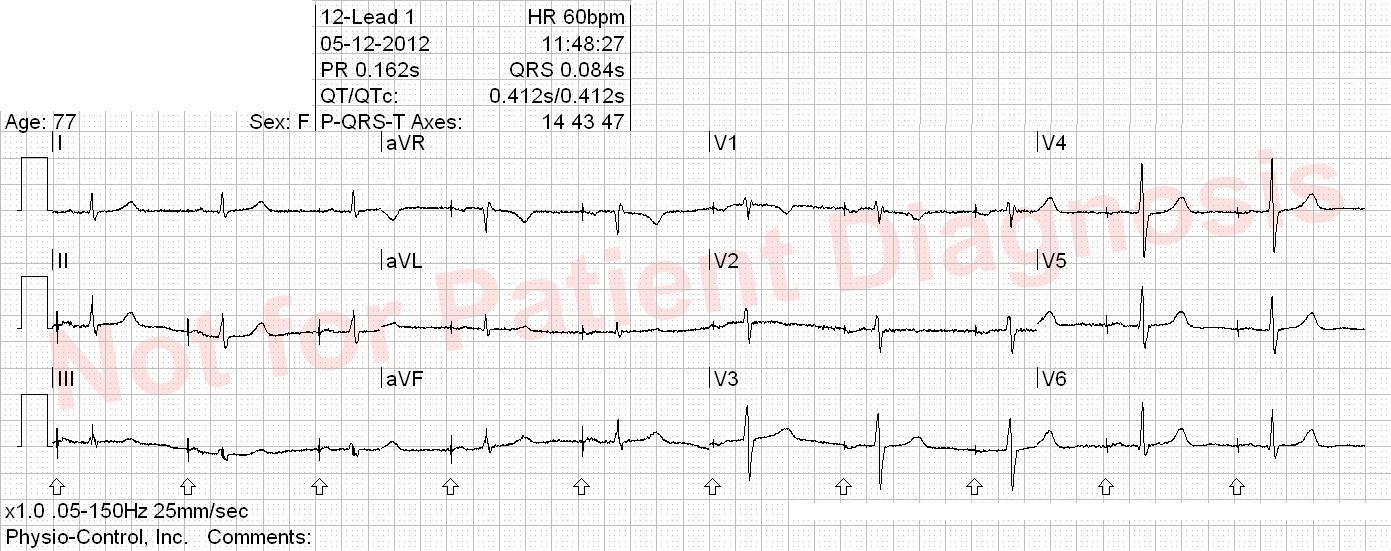
- VT = Ventricular tachycardia
- Afib = Atrial fibrillation
- AVRT = Atrioventricular reentry tachy
- AVNRT= Nodal AVRT
- RBBB = Right bundle branch block
- LBBB = Left bundle branch block
- WPW = Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
ECG Interpretation 2
15 March,2015 Antoine AyerQuiz-summary
0 of 50 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
Information
This electrocardiogram quiz contains several brief medical histories and their matching ECGs. For each question, you should check between 0 to 4 diagnoses. If the blood pressure is not specified, it means that it is in the normal range.
Remember: Do not use your browser’s “back” button. The result is shown only when you have answered every question.
Enjoy!
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 50 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-
You should improve your ECG skills to optimize your decisions regarding patient triage. You can find interesting educative resources in our link section.
You are welcome to retake the quiz ECG Interpretation 2 or continue to ECG Interpretation 3.
-
Congratulations! You passed “ECG Interpretation 2”.
Continue to ECG Interpretation 3.
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
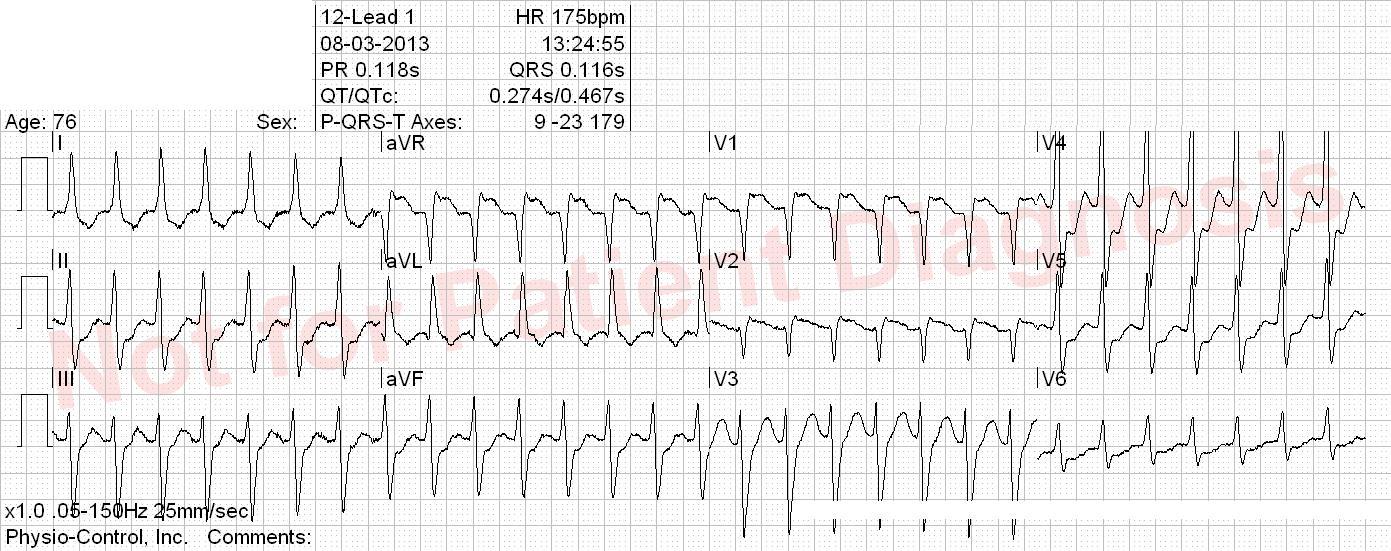
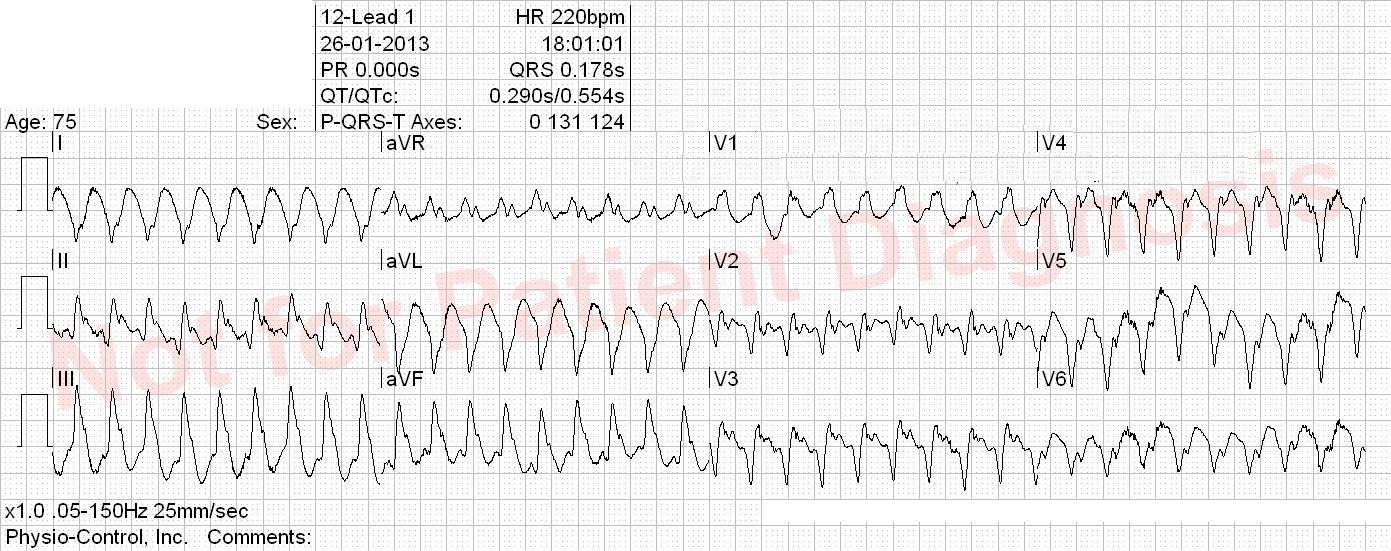
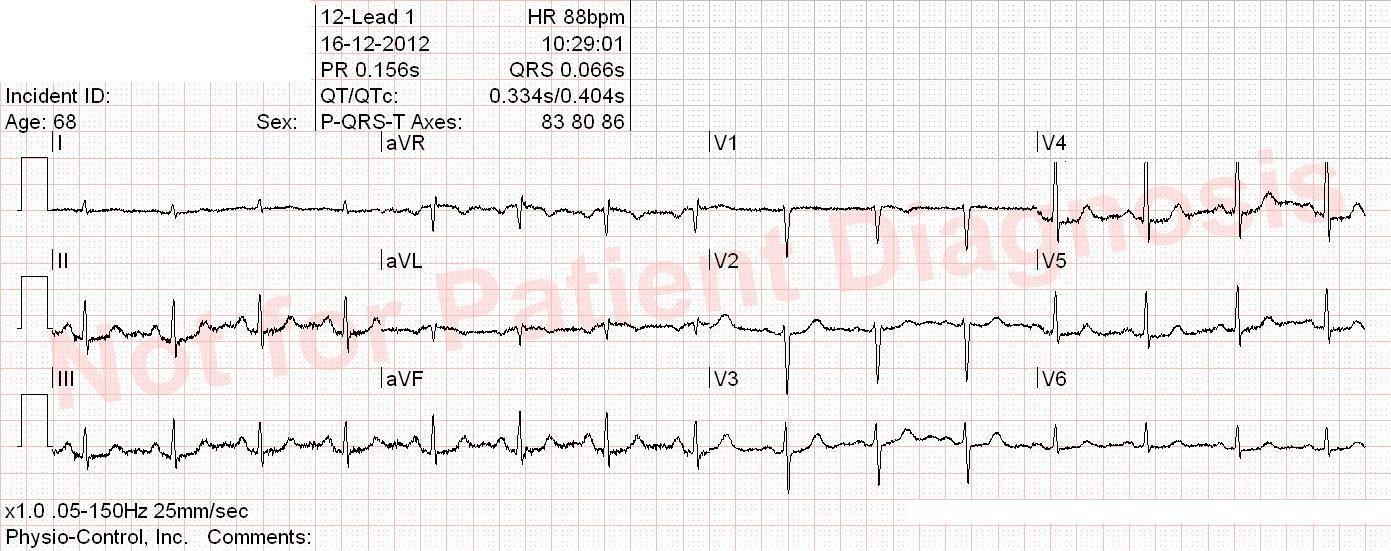
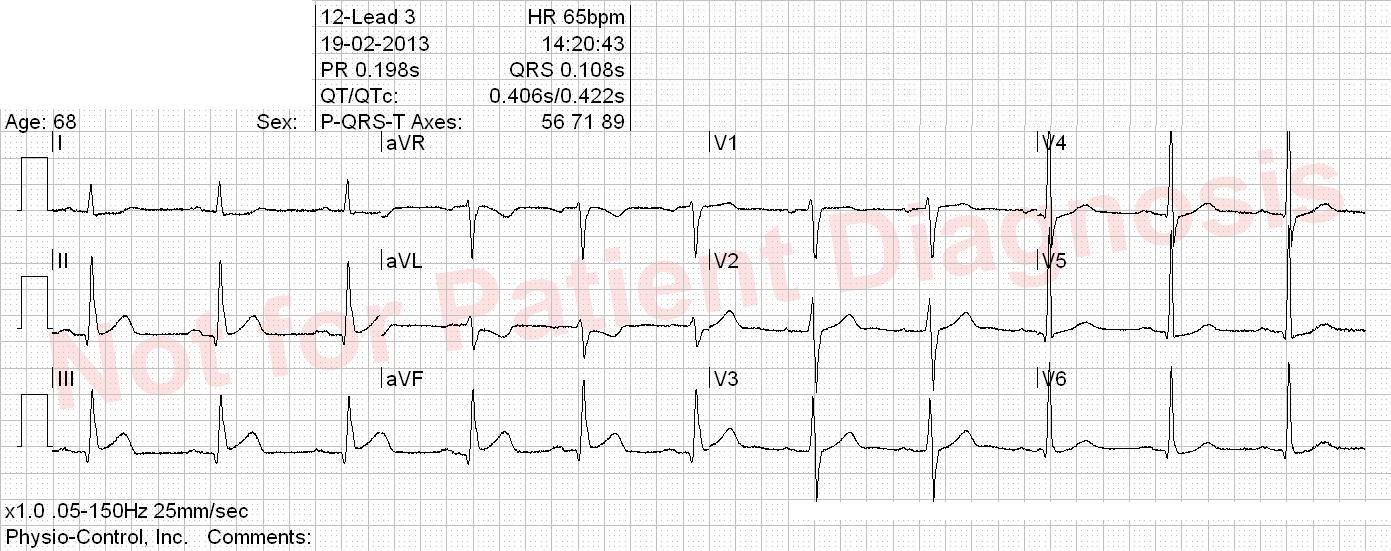
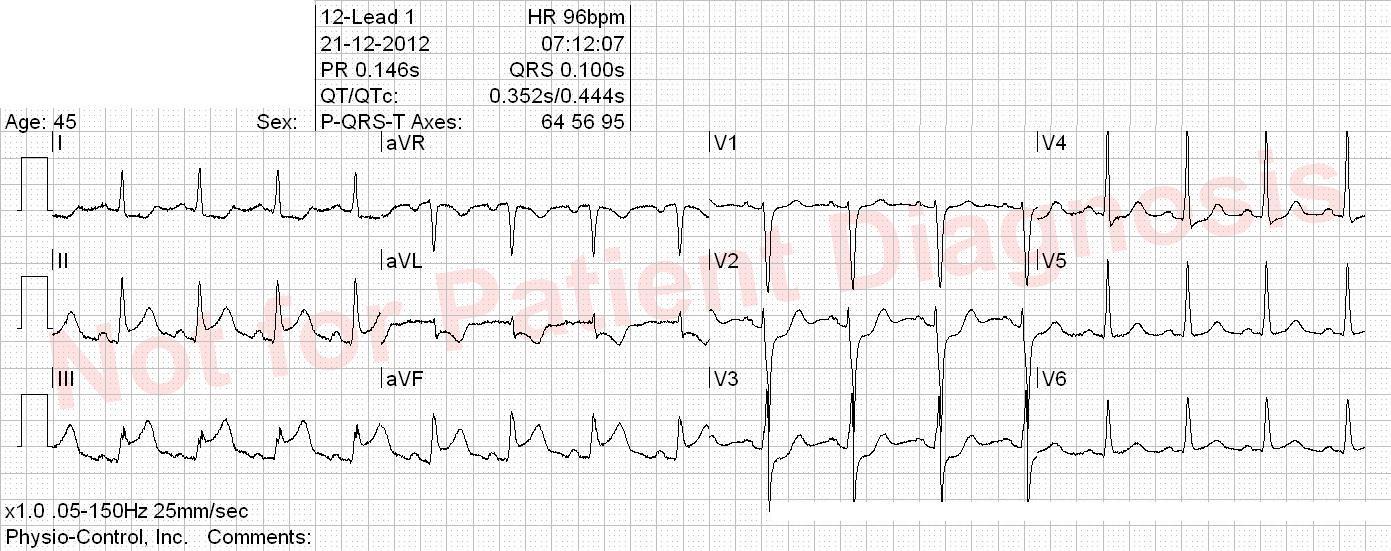
Patient with a biologic aortic valve and atrial fibrillation. Takes dronedarone. Suddent onset of palpitation, as well as chest pain and nausea.
Correct
Orthodromic AVRT (retrograd P-wave > 70 ms after QRS, see V1) most likely. Global repolarisation abnormities that does not fullfill STEMI criteria. The tachycardia should be acutely terminated and patient symptoms and ECG should be reevaluated for possible ischemia.
Incorrect
Orthodromic AVRT (retrograd P-wave > 70 ms after QRS, see V1) most likely. Global repolarisation abnormities that does not fullfill STEMI criteria. The tachycardia should be acutely terminated and patient symptoms and ECG should be reevaluated for possible ischemia.
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
Suddent onset of shortness of breath and chest pain, which started a few hours ago during a badminton game.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Cardiac arrest preceded by central retrosternal chest pain radiating the the left arm. Succesful CPR, awake and responding.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Diabetic known with hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Sudden onset of severe chest pain 5 hours ago.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
Had severe angina that started 5 days ago and lasted for 2-3 days. Now suddenly hemoptysis, severe dyspnea, hypoxemia….
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
Patient with dilated cadiomyopathy. Felt sick and sweating abnormally after exercising. Near syncope. Kendt DCM.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
History of prior CABG. Known with left bundle branch block. 3 days with shortness of breath, cough and fever. Normal BP.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Patient followed for aotic valve stenosis, is awaiting CABG + valve operation. Acute, central, opressive chest pain which started 3 hours ago. BP 70/40mmHg.
Correct
Although this ECG does not fullfil the criteria for STEMI, this patient history is very worrying and an evaluation in an hospital with a cardiothoracic surgery department should be undertaken.
Incorrect
Although this ECG does not fullfil the criteria for STEMI, this patient history is very worrying and an evaluation in an hospital with a cardiothoracic surgery department should be undertaken.
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
History of prior PCI of LAD. Patient is diabetic and has hypercholesterolemia. 1-2 hours with pain on the left side of the chest radiating to the left arm pit.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
Correct
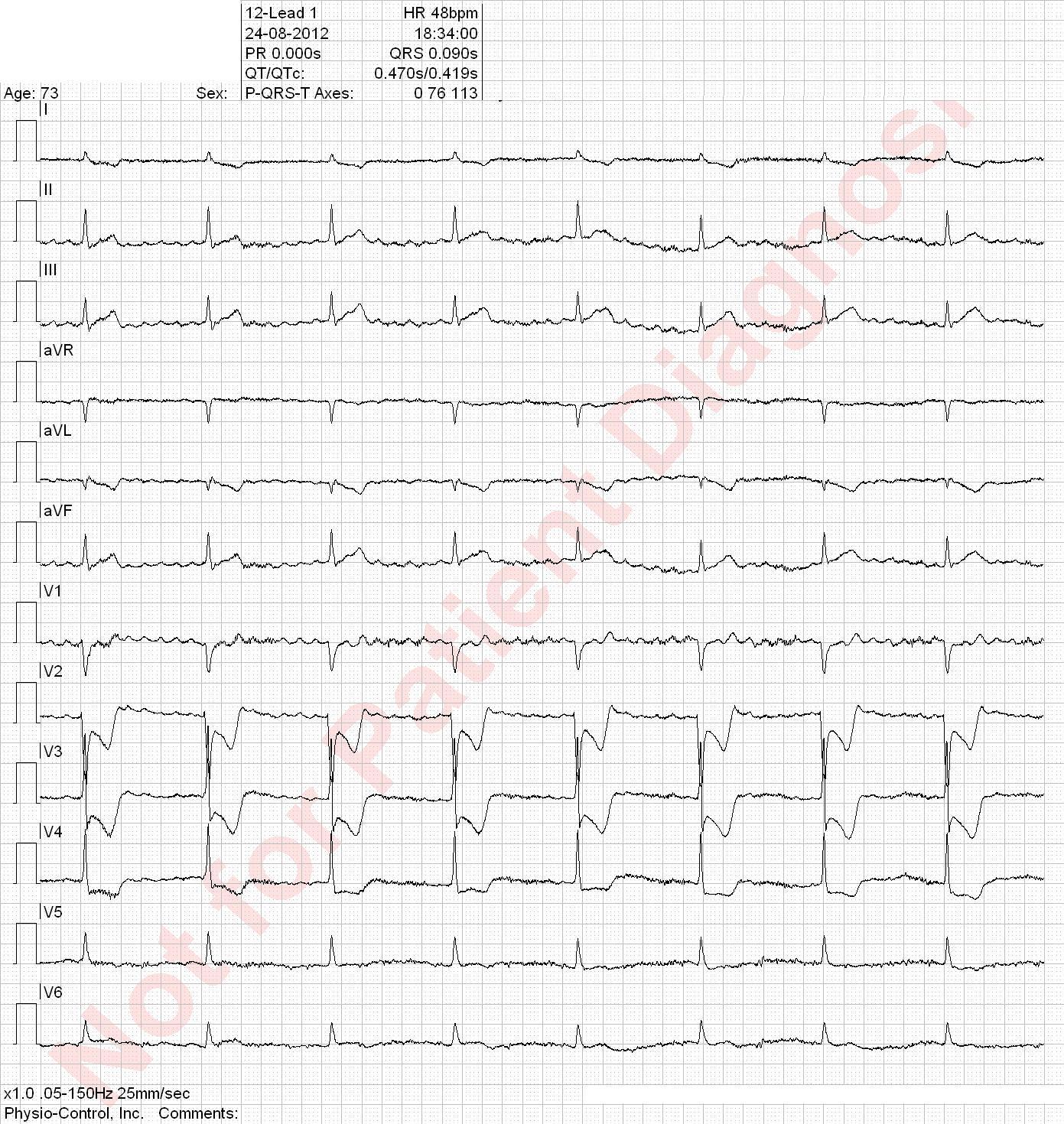
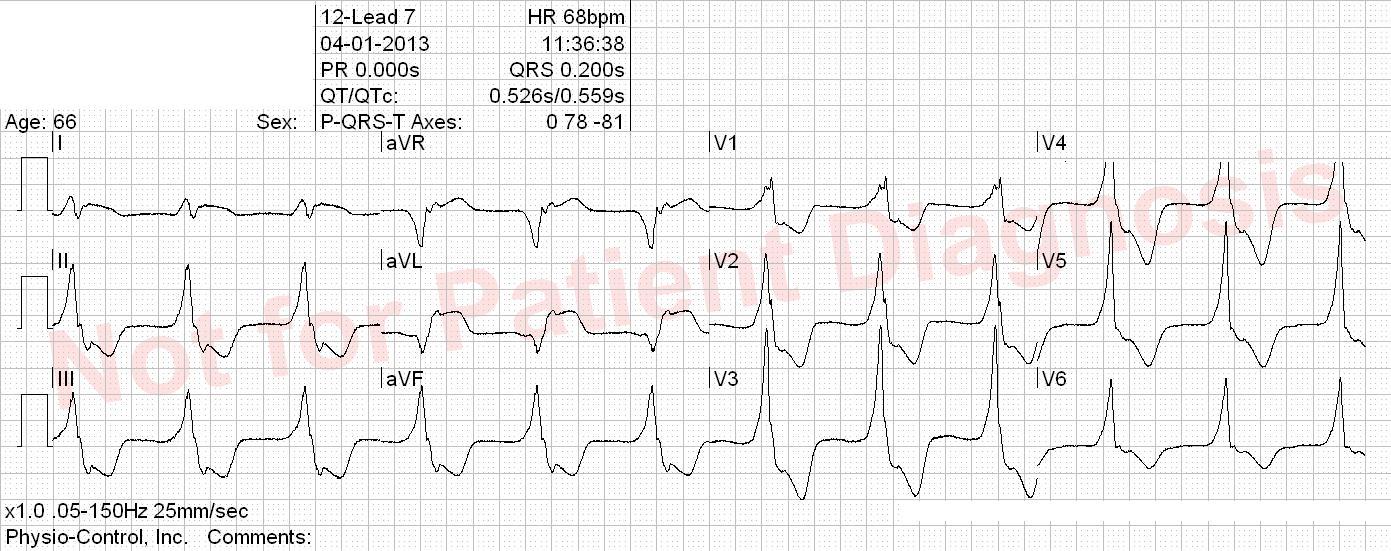
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm with fusion and capture at the end of the ECG. Anterior and inferior ST elevation. The ST segment cannot be interpretated in presence of an idioventricular rhythm. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is defined with a frequence between 50 and 110 bpm and is seen when ventricular activity superseeds sinus node activity. This rhythm is typically seen under ischemia/reperfusion and digitalis intoxication.
Incorrect
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm with fusion and capture at the end of the ECG. Anterior and inferior ST elevation. The ST segment cannot be interpretated in presence of an idioventricular rhythm. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is defined with a frequence between 50 and 110 bpm and is seen when ventricular activity superseeds sinus node activity. This rhythm is typically seen under ischemia/reperfusion and digitalis intoxication.
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
Wakes up in the middle of the night with increasing shortness of breath. At the end has also mild chest opression.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Patient with a history of atrial fibrillation and ischemic heart disease. 2 days with chest pain, shortness of breath and palpitation.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
Patient with ischemic heart disease. Increasing shortness of breath in a few days. Wakes up with exacerbation of his dyspnea. 3 syncopes.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Just discharged from hospital after a syncope of unknown origin. Now twitching and malaise. No angina, no dyspnea.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Woke up with central oppressive chest pain which are increase with deep inspiration and when lying on the back.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
Cardiac arrest after a period of shortness of breath and general malaise. Now open eyes and moves his extremities.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
Increasing pain between the scapula since yesterday, radiating in both arms, but especially the left one.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
Dement alcoholic with many cardiovascular risk factors, who complains of intemittent chest pain. Now pain free.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Several episodes of violent chest pain during the last 3 days. 2 episodes today associated with loss of consiousness.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
75 years old patient with hypertension and diabetes. Has chest pain which started an hour ago. BP 185/120mmHg. Improving after NTG spray.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
CABG in 2003. Chest pain since yesterday. The pain is aggravating after he had been working with a showel in the snow.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
Smoker but otherwise healthy patient with constant chest pain since yesterday evening. Meets at his GP. He is feeling really bad and has colds sweats. Normal BP.
Correct
Inferior Q wave , almost significant ST elevation inferior (<1mm)
Incorrect
Inferior Q wave , almost significant ST elevation inferior (<1mm)
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
Correct
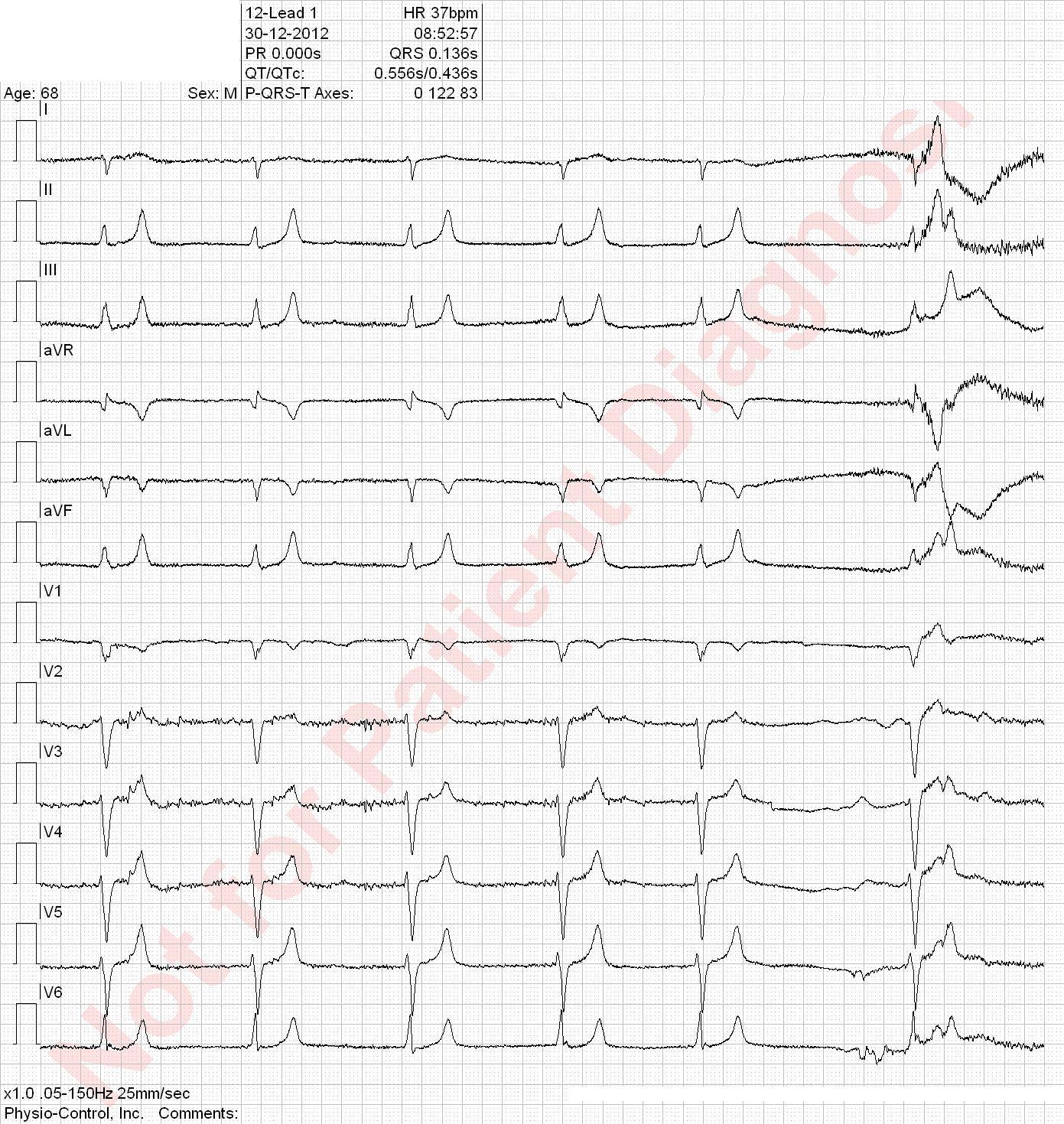
This patient has potential indication for pacemaker implantation.
Incorrect
This patient has potential indication for pacemaker implantation.
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
Know with an undefined heart disease. Central oppressive chest pain during the past two weeks. This night malaise and dizziness.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
Correct
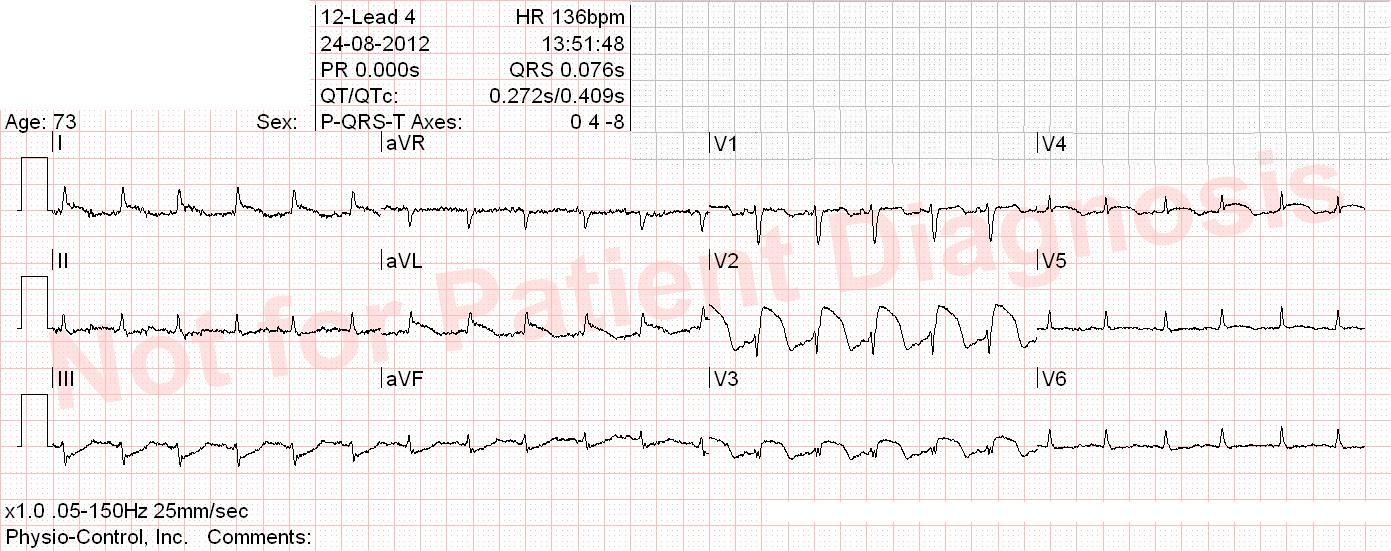
Right bundle branch block + strain. This patient had a plumonary embolism.
Incorrect
Right bundle branch block + strain. This patient had a plumonary embolism.
-
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
This patient had nausea when he woke up this morning but he has now severe chest pain which started an hour ago.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
History of previous AMI/PCI. Oppressive chest pain radiating to both arms which started 4 hours ago.
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
Young patient with one hour of palpitation, mild chest oppression and discrete shortness of breath and dizziness. Has had several similar episodes among the last few years.
Correct
Incorrect